Affine Transformation
仿射变换是在二维空间上对图像进行平移(Translation)、缩放(Scale)、旋转(Rotate)、错切(Shear)操作的组合。
四种变换的矩阵形式分别为:
平移:T_t = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & p_x \\ 0 & 1 & p_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
旋转:T_r = \begin{bmatrix} \cos\theta & -\sin\theta & 0 \\ \sin\theta & \cos\theta & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
缩放:T_s = \begin{bmatrix} T_x & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & T_y & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
错切:T_s = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & \tan\phi & 0 \\ \tan\psi & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
这几种变换组合之后,变换矩阵可以写成:
在这里,x、y和x'、y'分别代表变换前和变换后的点坐标。元素a_1到a_4代表旋转、缩放和错切这三种变换的组合,b_1和b_2代表平移,c_1和c_2代表透视变换,在仿射变换中是0。
可以看出,仿射变换的DOF=6,因此需要3个点对。要注意仿射变换矩阵应该是可逆的,如果不可逆,需要用一些方法去逼近这种变换。
仿射变换的特点是:相交线之间的角度可能发生变化,平行线之间的关系保持不变。
Perspective Transformation
透视变换,理解起来有些困难,文章[5]中给出了一个很浅显易懂的例子:
手电筒朝墙上打光,手电筒正着打,墙上光斑是正圆形,斜着打是椭圆形,近了打光斑变小,远了打光斑变大。透视变换就是通过投影的方式,把当前平面上的图像映射到另外一个平面。
和Affine Transformation很明显的一个区别是,Perspective Transformation是在3维空间进行变换的,因此变换得到的图像会具备一定的(3D)空间感。此外,透视变换不保证平行线之间的平行性,但是保证点之间的共线性。
根据上述公式Eq1,透视变换DOF=8,因此需要4个点对进行变换。
下图为这两种变换的差异提供了视觉上的直观表达。
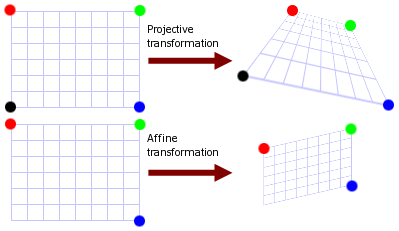
下图更详细地描述了Affine Transformation和Perspective Transformation之间的关联和差异。可以看出二者均属于Projection Transformation。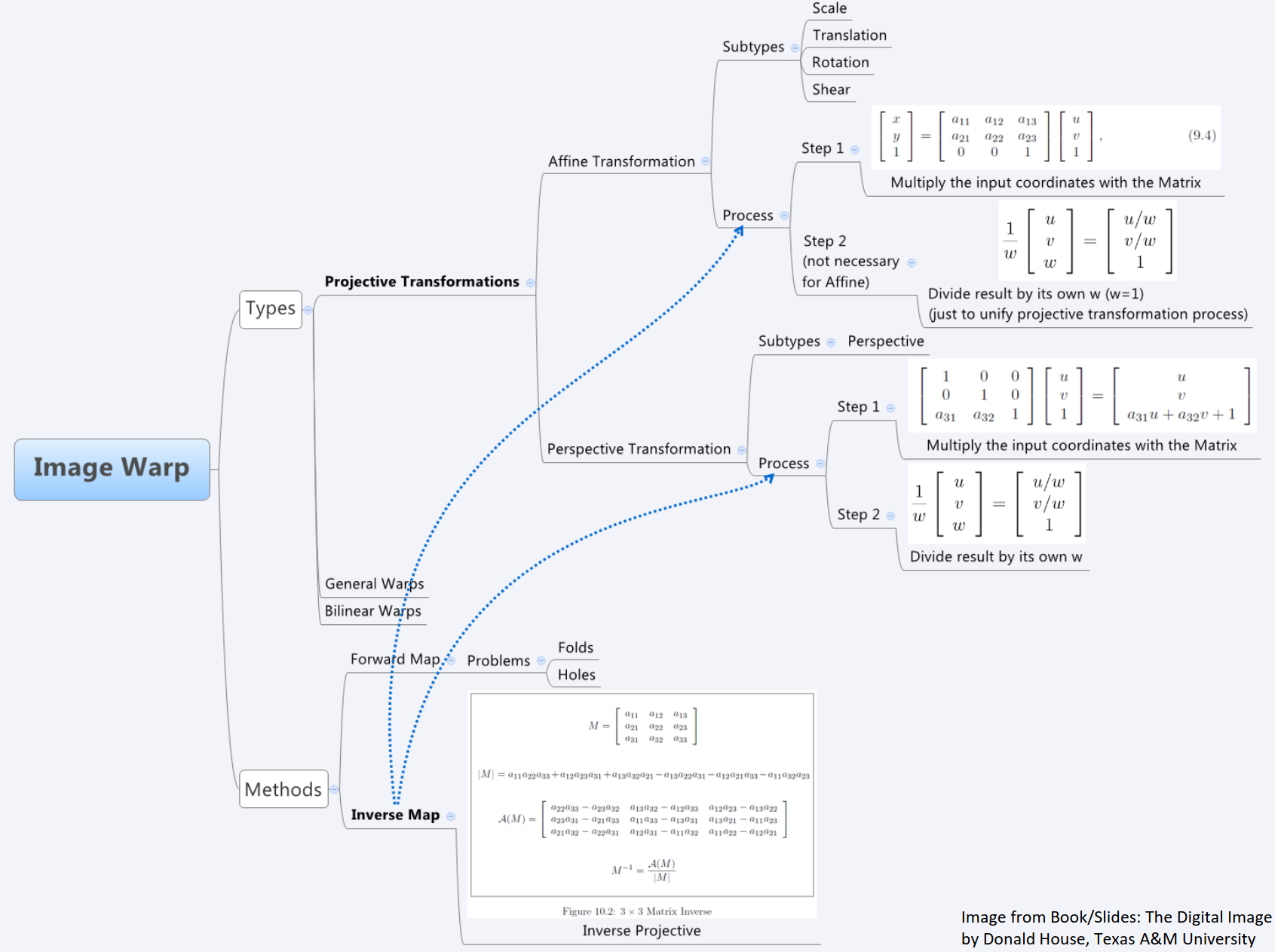
参考文章
[1] https://stackoverflow.com/questions/45637472/opencv-transformationmatrix-affine-vs-perspective-warping
[2] http://docdingle.com/teaching/cs545/presents/p12b_cs545_WarpsP2.pdf
[3] https://www.graphicsmill.com/docs/gm5/Transformations.htm
[4] https://blog.csdn.net/lx_ros/article/details/121413585
[5] https://amoko.github.io/2019/02/13/Affine-Perspective.html

